As you know, you cannot tan at home, even if the room is full of sunlight. The bronze tint to the body will be given by radiation called ultraviolet. This is the part of the spectrum located above the visible range. Infrared heaters for the home are often confusedly called ultraviolet heaters. This is fundamentally wrong. Ultraviolet heaters are not used to produce heat. But there are devices that have a dual function. Ultraviolet light gives the skin a golden tint in solariums and kills germs in medical institutions. Fashionistas wear glasses for a reason when they sit in a UV radiation device.
What is ultraviolet?
Ultraviolet, or UV, radiation occupies the spectral range between visible and x-rays from 100 to 400 nm. Ultraviolet was discovered after the discovery of infrared radiation with shorter wavelengths, lying at the opposite end of the spectrum. The main source of ultraviolet radiation is the sun.
Depending on the wavelength, there are three ranges of ultraviolet radiation:
- UV-A (315-400 nm);
- UV-B (280-315 nm);
- UV-C (100-280 nm).
UV-C and 90% of UV-B rays are absorbed by ozone, water vapor, oxygen, and carbon dioxide. Only 90% of UV-B and UV-A rays penetrate the atmosphere.
Difference between UV and IR rays
Both rays are part of the solar spectrum, and belong to its invisible part. However, this is where the similarities between them end.
Almost half of solar radiation is infrared radiation. They are characterized by the fact that they are a source of strong thermal energy, which is emitted by all bodies heated by them, including the human body.
Ultraviolet light not only heats, but also has a photochemical effect. It is absorbed by nucleic acids, which leads to a change in the vital activity of cells - the ability to grow and divide.
Ultraviolet Aquarium Sterilizer
A device used for cleaning aquariums is assembled from a small cylinder with two tubes inside for water inlet and outlet. An ultraviolet lamp is located inside this cylinder. The principle of operation of the device is that dirty water enters through one tube, undergoes disinfection from ultraviolet rays, and comes out through another tube, already purified. However, cleaning an aquarium with this device is not always effective because, for example, in large aquariums the device will not be able to collect water that is closer to the bottom of the aquarium, and it will remain partially dirty. And in salt water, due to its density, the device is generally useless.
This device is not recommended to be used on an ongoing basis, since ultraviolet rays destroy not only harmful bacteria, but also those that are beneficial for fish, snails and other inhabitants of aquariums.
The benefits of ultraviolet light
UV towel heater
Ultraviolet rays destroy certain types of pathogenic bacteria, viruses, and some fungi on different surfaces, in water and air. At the same time, UV radiation does not affect the habitat of these microorganisms.
Expert opinion
Grebnev Vadim Savelievich
Heating system installer
Infectious disease specialists warn that it is not always possible to achieve complete disinfection through UV radiation alone.
Other beneficial properties of ultraviolet radiation also include activation of the body’s production of vitamin D, which is critical for bone tissue. Radiation of this part of the light spectrum is necessary for the prevention of depressive conditions in people.
In addition, ultraviolet light, when used correctly:
- reduces blood viscosity;
- enhances microcirculation;
- strengthens the walls of blood vessels;
- reduces pain;
- improves the conductivity of nerve impulses, etc.
The opportunities that radiation provides are used to treat acute inflammatory skin diseases, purulent inflammations, etc. In such cases, ultraviolet irradiation (UVR) is prescribed.
This technology is also the basis for the operation of solariums, where you can get an artificial tan. Radiation is also used in dentistry to harden dental fillings.
Ultraviolet light is also used in other areas:
- mineral analysis;
- spectrometry;
- catching insects;
- restoration;
- chromatographic analysis;
- printing.
UV radiation in moderate doses is necessary for vegetation. But the flora dies from its excess.
Ultraviolet as a component of the light spectrum
The simplest example of electromagnetic radiation is sunlight. The spectrum of solar radiation is complex in composition, but it can be decomposed into 3 components - 3 groups of electromagnetic waves located in a certain range of lengths:
- light visible to the eye;
- ultraviolet radiation;
- infrared electromagnetic waves.
There are no questions about the definition of visible light - this is what allows the human eye to see surrounding objects in the daytime. If you pass daylight through a crystal prism, it becomes clear that white sunlight consists of seven main color components - red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo and violet, with fuzzy boundaries between them.
* A seven-color rainbow in the sky in sunny weather after rain is nothing more than the visible spectrum of sunlight, decomposed into components by refraction when passing through tiny drops of water in the air. The table shows the ranges of location of color components by wavelength, and it can be seen that the minimum wavelength is for violet radiation.
Ultraviolet radiation, by definition, consists of even shorter waves, the length of which is in the range of 10-400 nanometers, so it can be conditionally located below the violet segment. Electromagnetic waves of this length are not visible to the human eye, but a significant part of them (with a wavelength of 300-400 Nm) penetrates the protective ozone layer of the atmosphere, and their impact on the environment is significant, although the extent depends on the time of year.
Ultraviolet light is destructive to pathogens, but at the same time it is necessary for the process of photosynthesis of plants and the production of vitamin D in the human body, the lack of which causes the development of a serious disease - rickets. Small doses of ultraviolet radiation received by a person on the beach have a beneficial effect on the body, but an overdose of this natural factor will cause redness or even burns of the skin, and regular prolonged exposure provokes the development of cancer.
These characteristics of ultraviolet radiation determine its use primarily as a disinfectant and healing (in small doses) factor, and heating is just an inevitable concomitant factor of the influence of these electromagnetic waves.
Infrared (long-wave) radiation in the diagram is conventionally located above the red region of the spectrum and is also invisible to the human eye. But the result of exposure to waves of this length range occurs much faster than that of ultraviolet radiation; this effect is thermal. Long-wave radiation does not affect the transit medium, but acts directly on objects whose surface it reaches - the molecules of the object to a certain depth from the surface begin to vibrate, and the temperature of the object increases, in turn causing it to emit heat.
Harm from ultraviolet radiation
Radiation can negatively affect the condition of various objects made of polymers. Under its influence, various surfaces become dull, crack, and can be destroyed - this phenomenon is called UV aging. The longer objects are exposed to ultraviolet radiation, the sooner their properties are lost.
Susceptible to UV radiation:
- polypropylene;
- polyethylene;
- polymethyl methacrylate, or organic glass;
- aramid fibers, including Kevlar.
To prevent materials from deteriorating, substances are added to the raw materials that make the products resistant to such effects.
Ultraviolet radiation also has a detrimental effect on human health:
- when the skin's natural protective ability to tan is exceeded, burns occur;
- mutant cells are formed, resulting in the development of melanoma;
- intense radiation leads to radiation damage to the cornea (electroophthalmia).
Expert opinion
Grebnev Vadim Savelievich
Heating system installer
To protect the body from ultraviolet radiation, creams, eye lenses and glasses with UV filters are produced.
Types of ultraviolet devices
Today there are many devices that are called ultraviolet heaters, although they are not such. Most of these devices are made in the form of lamps of various designs. They are most often used in medical institutions, spa salons, kindergartens and others where disinfection measures are required.
Blue lamp
Germicidal lamp The
blue lamp, known to everyone since childhood, is an example of an ultraviolet heater for treating ENT organs and other parts of the body. The principle of its operation is based on local disinfection with an increase in the temperature of the irradiated area, for example, the ear.
In a blue lamp, ultraviolet radiation complements the effect of heat, and the resulting synergistic effect helps alleviate the disease, which leads to a speedy recovery.
Shoe dryer
Recently, new technologies have become a firm part of our lives and make life easier. This also applies to one type of ultraviolet heater in the form of a shoe dryer. This small device is made in the form of a block and consists of a built-in heating element and an ultraviolet lamp mounted around the perimeter of the device.
Infrared Gas Dryer
This dryer:
- Destroys all kinds of fungi, pathogenic microbes, heavy unpleasant odor emanating from the inside of shoes.
- Provides safe and effective conversion drying.
- Maintains the health and original shape of the shoes.
Towel warmer
Ultraviolet towel heaters are an integral part of modern SPA salons. They allow you to carry out hygiene procedures for body care at the highest level, in the form of compresses, rubs or pedicures, while using damp, warm, sterile towels.
With the help of such heaters, bactericidal treatment of glass, plastic and other products in the form of brushes, sponges, combs and many other small items is carried out, which, due to the properties of their materials, cannot be exposed to high temperatures or chemical disinfecting solutions.
In addition to the above devices, there are also a lot of different designs that use ultraviolet lighting for disinfection.
Such heaters combine the functions of heating objects and an ultraviolet sterilizer.
Sterilizer - heater
For example:
- In hairdressing salons, where the master's tools are processed in special devices.
- In solariums, where you get an artificial tan in the middle of winter, which not only decorates fashionistas, but can be used for certain skin diseases.
- Such devices are widely used in dentistry. But when using them, it is necessary to protect your eyes with opaque glasses to avoid burns to the cornea.
- Modern innovative technologies make it possible to use ultraviolet radiation for the benefit of humans, and first of all, in the fight against pathogenic viruses and bacteria.
Due to the photolytic reaction, ultraviolet light:
- Damages their cell membranes.
- Prevents their cell division.
- Breaks all bonds of their organic molecules.
An important property of ultraviolet light is that it affects living cells of viruses and bacteria without affecting their habitat where they are located. This feature is extremely important for the disinfection of water, household items, sterilization of premises and medical equipment.
Is there ultraviolet heating?
The answer is clear - no, unlike infrared. But ultraviolet light still found application in everyday life.
"Blue" lamp
The device is also called the Minin reflector, named after the Russian military doctor who first used ultraviolet light to treat patients.
Lamps are still used today for the complex treatment of various diseases of the skin, nasopharynx, ear, etc. - for ARVI, otitis, sinusitis, etc. For treatment, the lamp is directed to the problem area. The rays increase the temperature of tissues and destroy pathogenic microflora. After a course of procedures, pain decreases and inflammation decreases.
Until the early 40s of the last century, a Minin lamp was in almost every home. Such popularity of the physiotherapeutic method was explained by the absence or shortage of necessary medications. But after antibiotics and sulfonamides became widely used, the popularity of the device began to decline.
Shoe dryer
Ultraviolet shoe dryers are gradually becoming as common a gadget as blue lamps once were.
They are lasts that are inserted into shoes. They contain a heating element powered by electricity and a UV lamp.
Manufacturers claim that in addition to drying wet shoes, such devices disinfect the lining and insole, destroying all types of fungi, and eliminating unpleasant odors.
Towel warmers
Ultraviolet towel heaters are installed mainly in modern spa salons. They allow you to disinfect textiles used for compresses, rubbing, pedicures, etc.
Recently, smart gadgets have appeared on sale. They have built-in sensors that react to a person and turn off the ultraviolet light if the distance between him and the device is reduced to 2.5 m.
Similar equipment with an ultraviolet disinfection function is used for other accessories that come into contact with skin, hair, nails - brushes, sponges, combs, etc., which cannot be disinfected with chemicals and high temperatures.
UV sterilizer for aquarium
The device is installed in aquariums to purify water from harmful organisms. An ultraviolet sterilizer is a small cylinder on the surface of which there are two tubes - inlet and outlet. Through the first, water enters the cylinder and is exposed to UV irradiation; through the second, it exits purified. Such sterilizers are effective only in fresh water and only in small aquariums.
UV lamps for mosquitoes
Ultraviolet light is also used in the fight against mosquitoes, since this range of the spectrum attracts insects. When mosquitoes fly up to the device, they land on the grille that surrounds the housing. An electric current is connected to it, destroying insects.
Ultraviolet devices are a useful gadget in the home when it comes to disinfection and treatment. But you cannot use them as a heater for heating rooms, since it can harm your health.
Pros and cons of ceiling heating
Among owners of private households, there is a very old, but very persistent myth that the heating system should be located in the lower third of the walls of the room, or, in extreme cases, on the floor, and certainly not on the ceiling. It is believed that in this case, warm air is evenly distributed throughout the room and does not create local overheating zones.
With the advent of the first ultraviolet and infrared heaters, attitudes towards ceiling heaters changed significantly from negative to positive. A red-hot nichrome spiral with a reflector made it possible to direct the flow of heat to almost any place.
In fact, installing heating radiators on the ceiling provides serious advantages:
- The ceiling heater is located outside the area of human movement, there is less chance of getting caught or broken, accidentally touching it and disabling it;
- Unlike floor and wall heaters, a ceiling heating system does not heat the floor and walls, but most importantly, the comfort zone.
This is approximately 120-200 cm from the floor level. Everything that is not included in the comfort zone heats up noticeably less, which means fuel or electricity is saved. A ceiling electric heater removes a significant part of the condensation that falls in the ceiling area and directly on the floor in an unheated room.
Infrared heater
In addition, such systems can be located, as they say, pointwise, for example, above the workplace, in the kitchen or in the rest room, above the sofa or bed. It seems like a small thing, but again, ceiling heating at a distance of a meter is noticeably more effective than if you install any other type of heater on the opposite wall of the room.
Of course, ceiling heaters also have a number of significant disadvantages. Firstly, it is much more difficult to repair, configure and maintain an electric or gas appliance installed on the ceiling than on a wall or floor. Secondly, no matter how efficiently energy is directed throughout the entire volume of the room, a certain part of it is spent on heating the ceiling, which is not always justified from an economic point of view.
In addition, a ceiling-mounted UV heater operating in the ultraviolet range or a gas burner are not as safe for human health as conventional electric fireplaces and ceramic tiles.
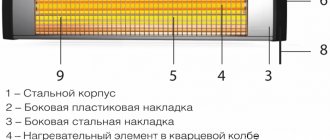
UV heater