Power surges can cause serious damage to any household appliance. To avoid having to spend money on frequent repairs, or even worse, buy new equipment, manufacturers have come up with simple protection in the form of a fuse. It takes the full impact of the voltage drop and burns out, saving the more significant parts of the device from such a fate. Subsequently, you only need to replace this inexpensive part, and any equipment will work like new. However, not everyone knows where it is. Therefore, replacing the fuse in a microwave will be discussed in detail below.
Microwave oven device
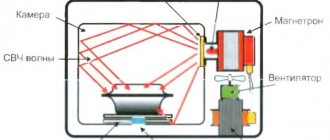
The heart of a microwave oven is a magnetron, the antenna of which supplies high-frequency waves to a special chamber. This radiation passes through a waveguide that transmits radio waves only at the operating frequency (2.4 GHz). It is protected from the ingress of fat and food particles during cooking by a special lid made of mica. The property of this material is such that it easily transmits high-frequency radiation, but does not conduct back electricity, which can arise as a result of improper operation of the furnace . Namely, this phenomenon is fraught with failure of the magnetron.
The operating principle of a microwave oven is as follows. The food, slowly rotating on the plate, is evenly processed by the flow of electrons, which affect the water included in its composition. This process is accompanied by the release of heat, which helps to warm up the food. The design of the chamber is designed in such a way that radiation cannot escape beyond its boundaries, which means it is safe for humans, whose body, as is known, consists of 80% liquid.
Important! In order for the magnetron to generate its waves, a high-voltage transformer is included in the microwave circuit, which provides the lamp with the required voltage. It is this part of the furnace that is most vulnerable to power surges in the household electrical network.
Circuit breakers
A fuse is an element of protection for an electrical circuit. Nowadays, almost all electrical devices are equipped with such elements and microwave ovens are no exception. There are many types of fuses, differing from each other in the operating principle, and one of them is a fuse link. For electrical protection, this type of fuse is used in microwave ovens - a fuse. The operating principle of the fuse is based on the metallurgical effect. Such a fuse in its design contains a thread made of a low-melting material - metal. If the permissible current flowing through this thread is exceeded, the thread heats up to the melting temperature of the metal from which it is made and is destroyed. In this case, the electrical circuit is broken and the device is de-energized. The permissible amount of current that the thread can pass through itself without destruction directly depends on its cross-section and the properties of the material of manufacture. To protect adjacent structural elements of electrical equipment from splashes of molten metal formed when the filament breaks, the filament is placed in a glass or ceramic tube. And, for ease of installation, metal caps are put on this tube at the ends, which are fuse contacts. This is exactly how we are used to seeing a fuse today, in the form of a tube with shiny caps.
Read also: Current 16 amperes how many kilowatts
The design of a microwave oven most often contains three fuses. Figure 1 shows one of the options for the location of fuses inside the furnace.
- Mains fuse. It is located, as a rule, on the network filter board, schematically - at the furnace power input. Through this fuse, all circuits of the device are powered. The protective actions of any fuse are bidirectional. It’s the same with the mains fuse: on the one hand, it protects the furnace itself from power surges, and on the other, it protects the supply network from short circuits that can occur when various types of malfunctions occur in the furnace design. Having a fairly large rating - 8 - 12A, the mains fuse weakly protects the oven electronics from voltage surges, but does a good job of protecting the network from microwave malfunctions.
- High-voltage fuse – is an element of protection of the high-voltage power supply circuit of the magnetron. It protects, first of all, the high-voltage transformer from overloads that occur in the event of failure of the elements of the multiplier or the magnetron itself. Structurally, the high-voltage fuse is located next to the transformer, and schematically, it is included in the open circuit, between the output of the high-voltage winding and the input of the multiplier. High voltage circuits have special safety requirements. Therefore, the conductors of this circuit have reinforced double insulation, and the fuse is hidden in a special plastic casing. Housings can have different designs and shapes. But, they almost always consist of two halves, connected to each other by a plastic jumper on one side and latches on the other. If you disconnect the latches, the casing opens like a box, providing access to the fuse itself (Figures 2,3,4).
There are furnace models in which there is no high-voltage fuse as such - it is not provided by the manufacturer. In such cases, the function of protecting the high-voltage circuit is performed by the mains fuse. In order for the mains fuse to trip when the elements of the magnetron power circuit fail, the load on the transformer must more than double and for a fairly long period of time, which clearly has a bad effect on its health and can lead to failure of the transformer.
- The presence of a third fuse is typical only for furnaces with an electronic control panel. Each electronic panel is powered by its own separate power source. The basis of such a source is a low-power power transformer, which converts the network voltage into voltages suitable for powering the panel circuits. The primary winding of this transformer is powered from the network through a separate fuse, which is structurally, most often, an element of the design of the transformer itself. In other words, this fuse is located on top of the primary winding and is covered with insulation on top. This arrangement makes it much more difficult to replace the fuse if it fails. But it often happens differently, for example, in Samsung ovens, this fuse is located separately on the control panel board and replacing it, if necessary, is not difficult. This fuse has a very small rating and is very sensitive to voltage instability in the network.
When the high-voltage fuse trips, the oven will “pretend to be working”, everything will function except the magnetron, that is, everything will make noise, burn and spin, but it will not heat. But when the mains fuse or the control panel fuse trips, the effect will be approximately the same - the oven will be completely silent.
Life teaches you not to skimp on safety, so if any of the fuses blows, it is always better to look at its rating on the cap and replace it with the same one. But, if you still decide to install the “beetle”, then I beg you, do not under any circumstances use nails or other conductive objects that are suitable in size for this, and do not do it as shown in Figure 5 on the left - this is not it won't lead to anything good. Don’t be lazy, use the table for calculations, and do it as shown in Figure 5 on the right, believe me, it will be better.
Read also: How to check a Schottky diode with a tester
| Filament destruction current, A | Wire diameter, mm | |||
| Copper | Iron | Tin | Lead | |
| 0,5 | 0,03 | 0,06 | 0,11 | 0,13 |
| 1,0 | 0,05 | 0,12 | 0,18 | 0,21 |
| 2,0 | 0,09 | 0,19 | 0,29 | 0,33 |
| 3,0 | 0,11 | 0,25 | 0,38 | 0,43 |
| 4,0 | 0,14 | 0,3 | 0,48 | 0,52 |
| 5,0 | 0,16 | 0,35 | 0,53 | 0,6 |
| 6,0 | 0,18 | 0,4 | 0,6 | 0,68 |
| 7,0 | 0,2 | 0,45 | 0,66 | 0,75 |
| 8,0 | 0,22 | 0,48 | 0,73 | 0,82 |
| 9,0 | 0,24 | 0,52 | 0,78 | 0,89 |
| 10 | 0,25 | 0,55 | 0,85 | 0,95 |
| 15 | 0,32 | 0,72 | 1,12 | 1,25 |
| 20 | 0,41 | 0,87 | 1,35 | 1,52 |
| 25 | 0,46 | 1,0 | 1,56 | 1,75 |
| 30 | 0,52 | 1,15 | 1,77 | 1,98 |
The table, according to approximate calculations, shows the physical parameters of the threads of homemade fuses made from various materials. This is not an example of how to do it, but a fuse restored using the data in this table is still better and safer than a nail.
Electricity is a good thing, but every double-edged sword, remember this. When repairing electrical devices, be careful, follow safety precautions and do not neglect the safety features. Good luck with the renovation!
This household appliance is an indispensable assistant for the housewife in the kitchen: with the help of a microwave you can quickly heat up food prepared the day before, as well as stew vegetables and meat products, make original hot sandwiches and much more. Like all appliances, a stove can break down; the most common fault is a fuse blowing due to a power surge. We will tell you in detail what kind of fuses there are in a microwave oven, and also provide a replacement algorithm.
The purpose of fuses in a microwave oven
The fuse is a metal thread passing through a glass or ceramic bulb. It is covered with a protective sheath so that when a thin wire burns, molten splashes do not damage other parts.
Kinds
There are three types of fuses installed in a microwave oven:
- network;
- high voltage;
- for electronic control.
Purpose
The mains fuse serves as protection against both voltage surges and short circuits. It is installed directly on the input cord. The part can be considered universal, since it responds to any danger, disconnecting the microwave oven from the network.
The high-voltage fuse provides protection exclusively to the main components of the furnace - the transformer with the magnetron. In case of network congestion, it cuts off power only from these nodes. Therefore, when a part burns, it visually looks like the oven continues to work: there is lighting and sound, the table even rotates, but the product does not heat up. This fuse is located near the transformer. It is enclosed in a separate plastic case with latches. In some cases, when a high-voltage fuse blows, it can trip the circuit breaker on the common panel, which will cut off power to the entire house.
The control module generally requires little voltage. Therefore, to protect the unit, another plug is installed on top of the primary winding of a separate low-power converter that powers the electronic control panel. It is quite difficult to change it, since the part is specially insulated. But in Samsung models, the fuse is located directly on the control module board, which makes access to it much easier.
Before you buy a microwave oven, you need to check which fuses are on the selected model. Some manufacturers do not install high voltage protection on their products . For example, Sharp models do not have it. Therefore, only one fuse will provide protection against all possible threats - the network fuse. And in some cases this is not enough.
Important! The function of the mains fuse is to turn off the magnetron only in the event of a fairly long period of exposure to double load on the transformer. This time is often enough for the two most important components in a microwave oven to fail.
How many are there in the microwave?
The microwave is protected by three fuses.
Read also: Co 206 drum type machine instructions
- Network defender. This type of fuse is located at the power input and protects the entire device from possible voltage surges, which are not uncommon in our city networks. It also protects your home network from short circuits that may occur inside the oven. As a rule, it has a high potential - up to 12A, and if various malfunctions occur inside the product, the microwave instantly disconnects from the network.
- The high-voltage version serves as a protection element for the magnetron, protecting the high-voltage transformer from possible overloads. It is located nearby, and according to the diagram it is designed to break the circuit between the input and output of the high-voltage unit. Such circuits in technology are constantly subject to exceptional safety requirements, therefore all conductors of the high-voltage circuit are double insulated, and the safety element itself is enclosed in a separate housing made of hard plastic, which has different shapes and colors. It consists of two halves connected by a jumper and latches - they prevent spontaneous opening of such an original container. To replace the fuse, you need to release the latches, remove the part with the burnt core and insert a new element.
- Another fuse of a similar class is installed only on microwave models with an electronic control panel, which is powered from a low-power power transformer. It converts electrical current from the home network into the voltage needed to power electronic circuits. A separate circuit protector is at the same time a structural element of the entire unit, or, in language understandable to the user, it is located on top of the primary winding and is covered with special insulation, so it is quite difficult to change it. If you have a Samsung oven, then this part is located separately - on the control panel board, which makes the work much easier.
The instructions for the equipment will help you find out which fuses are on your stove model. Many modern models of microwave ovens do not have high-voltage fuses - manufacturers simply do not install them during manufacturing at the factory, so all their functions are performed by the network protector. But it burns out if there is a problem in the magnetron circuit only when the transformer is subjected to double load for quite a long time.
Such impacts negatively affect the transformer, and quite often lead to its premature failure.
Another interesting feature that few users know about: when the high-voltage protective element burns out, all parts except the magnetron will work: the circle will spin, the product will make operating noise, but will not heat up. If the mains fuse or control panel blows, the microwave does not react in any way to your actions - all attempts to turn it on are null (for more details, see the article on what to do if the microwave does not turn on).
Causes of burnout
As mentioned above, fuses burn mainly due to a sudden surge in voltage in the household electrical network, which provokes an overload of the circuit or a short circuit in the turns of the transformer coil. These processes trigger the protection, which occurs by interrupting the contacts in the circuit and disconnecting the microwave from the network. This is necessary not only to preserve the integrity of the more important parts of the stove, but also to prevent a fire hazard in the house.
But there are times when the fuse burns out during a certain action. For example, when opening the microwave door. This situation occurs in ovens of many brands, but most often Samsung and LG models suffer from this. The problem is the door microswitches. Any microwave has three of them, and according to the safety protocol, they are triggered in turn to automatically stop the oven when the chamber is fully opened. This measure is necessary to prevent radiation from penetrating outside. And when particles of fat or carbon deposits get on the springs of the microcontacts, they weaken, which can also happen even simply from prolonged use. Because of this, the switch does not operate and the fuse burns out.
But if the protection is triggered when the microwave oven is turned on, and replacing the fuse does not help, then the problem is most likely a damaged high-voltage diode. This has often been observed with Panasonic models. This can happen when there is a short circuit in the windings of the transformer or inside the magnetron.
Replacing the fuse
Replacing a blown fuse is usually not difficult (except in some cases with control module protection). But getting to it and performing some actions related to safety for health and life may seem like a problem for inexperienced craftsmen.
Disassembling the microwave
It's actually simple:
- unplug the oven power cord from the socket;
- find all the bolts on the back cover and unscrew them;
- remove the casing;
- we are working on fuses, but without haste, since if you need to inspect the magnetron, you will have to remove the transformer and air duct.
Advice! To work safely with fuses, it is necessary to perform one more operation - discharge the capacitor.
Capacitor discharge
The electrical circuit of the microwave contains a resistor that automatically discharges the capacitor when the device is disconnected from the network. In fact, it may be absent, or if it is available, it may not function. It is strongly not recommended to ignore these precautions and carry out work inside the oven with bare hands, since even when the power is turned off, the capacitor retains the accumulated voltage (and not a small one). And only if you are completely sure that it is discharged can you safely carry out repairs.
Important! Disconnecting the microwave from the power supply does not guarantee complete safety during repairs. Many parts inside retain residual stress for a long time. Electric shock can be not only painful, but sometimes fatal!
There are enough recommendations on how to discharge a capacitor. It is generally advised to close the contacts using a screwdriver. But this method is not approved by professionals: sparks and even failure of the capacitor are possible, not to mention a melted screwdriver. Experts suggest using a separate resistor with a resistance of 20 ohms. Or you can remove the discharge using a regular light bulb.
Replacing the fuse
Even when the capacitor is guaranteed to be discharged, it is not advisable to change the fuse with bare hands. You need to use current-insulated tweezers or a screwdriver with a well-insulated handle. The replacement algorithm is as follows:
- make sure that the device is disconnected from the network;
- Using a tool, remove the fuse that has burned out from the socket;
- install a new one;
- We assemble the stove and check its functionality.
As you can see, it only takes a few seconds to replace a part. More time is spent on preparation and compliance with safety measures. And to be completely sure, you can watch the training video.
Tags: Samsung microwave, microwave repair, microwave fuse
Comments 69
I disassembled and threw away the microwave in the same way. I only left the transformer from it, I’ll probably do resistance welding.
Well done of course! But! if it burns out again, be sure to remove the middle door mic, I probably saw them inside when I removed the panel, 3 of them, two with two wires, and one with three, here is the one with three, you can take it apart and look, usually there is carbon deposits on the contacts inside it
it was possible to solder 1 thin wire to a relative and then the repair would be completely free