Microwave ovens have become such a part of our daily lives that today it is difficult to imagine an apartment or house without this useful appliance in the kitchen. The functionality of microwave ovens allows you to perform a wide range of work related to the thermal processing of food: defrosting, heating and even preparation. You may not know this, but they can also be used to disinfect rags and sponges that do not contain metal. In this article we will look at how microwave ovens are designed and what the principle of their operation is.
Historical reference
As is often the case with useful and ingenious inventions of mankind, the benefits of microwave waves for domestic use were discovered completely by accident. This happened in 1942, where physicist Percy Spencer was studying the properties of devices with microwave radiation.
According to one version, the scientist accidentally placed a sandwich on the installation and discovered after a couple of minutes that it had warmed up throughout its entire thickness. Another version says that a chocolate bar melted in Spencer’s pocket and he, happy with his discovery, immediately ran to the store; after some time, the scientist observed how microwave waves turned the fresh corn he bought into popcorn in a couple of seconds.
In 1945, Percy Spencer patented the technology for using ultrahigh-frequency waves in the food industry, and two years later the first devices similar to modern microwaves appeared in American military hospitals and canteens. It is worth mentioning separately that these units, unlike modern ones, really resembled stoves, since they weighed about 340 kg.
Subsequently, the development and introduction of microwave ovens to the household appliances market was taken over by the Sharp company, which owns the main revolutionary achievements in this industry:
- in 1962 they mass-produced the first household microwave;
- in 1966 - they began to equip the stoves with a rotating stand-table;
- in 1979 - released the first microprocessor-controlled device;
- in 1999 - they created the first model of a microwave oven with the ability to connect to the Internet.
Today, the household appliances market offers a huge variety of microwave ovens with a wide variety of functionality, but all of them are simple, economical and safe for health.
How it works?
Surely many of us, at least once in our lives, have been interested in what the operating principle of a microwave oven is based on and how it turns out that food placed in it warms up quite quickly.
The fact is that the products we use for cooking contain water, fat, mineral components, and sugar in various proportions. All of these substances contain dipolar molecules in their structure, which means that one of their ends is positively charged and the other negatively charged. Meat, grains, vegetables and any food product in general contain a huge amount of such molecules.
Let's remember physics - in the absence of an electric field, dipolar molecules are in a disordered position. As soon as a substance is exposed to an electric field, the molecules are rearranged and “stacked” according to the direction of the lines of force: the positively charged ends are towards the “plus” pole, and the negative ends are towards the “minus”. Accordingly, when the polarity of the electric field changes, the molecules will begin to “unfold” 180˚. The operating principle of a microwave oven is based on this phenomenon.
So, on average, the operating frequency of a microwave oven is 2.45 gigahertz. This means that 1,000,000 oscillations (switchings) occur in one second. During one such switching, the polarity of the electric field inside the microwave changes twice - from “plus” to “minus” and back. A simple mathematical calculation tells us that in one second, the electric field into which we place food changes polarity 4.9 million times. That is why these devices are called microwave ovens - the decoding of the abbreviation reveals the word “ultra-high frequency”. In fact, we force the molecules to rotate at a very high speed, as a result of friction from each other, heat is released. The upper 1-3 cm of the substance is exposed to the electric field, from which heat spreads deeper. That is why, when cooking some products in a microwave oven, it is recommended not to turn it on “full”, but to select medium power and increase the processing time.
How does a microwave oven work?
The choice of microwave ovens was made in post-war America. The legend goes that an engineer accidentally discovered a chocolate bar in his pocket that had melted under the influence of high-frequency electromagnetic waves. Gradually, the scientist came up with a microwave oven.
Another legend says: devices were invented in Germany. One of them was the microwave oven: during the division it went to America. Radiation at 2.4 and 5 GHz is not used in professional communications - it is absorbed by water and steam.
That is why Wi-Fi and cellular communications (the latter not completely) operate in the above mentioned ranges. Such waves are not needed due to high losses. Scientists have found out that water molecules, due to mysterious properties, suck out the energy of the wave. The molecule has a magnetic moment, which the field grabs and begins to chaotically rotate two hydrogen and oxygen, held together by an indestructible bond.
This is interesting! Scientists conducted an experiment on freezing water that passed through the microwave compartment. It turned out that the growth of regular snowflake crystals was disrupted. It’s time to remember Tesla’s theories: the Universe consists of a set of harmonic oscillations. Exposure to electromagnetic waves disrupts natural processes.
When turned on, the smallest particles begin to move very quickly: they instantly heat the food by volume. The process occurs due to the significant water content. Place the biscuits inside; the heating process will be slow. Anyone who has an induction hob at home has figured out why you can’t put metal utensils or plates with a gold rim inside. Foucault currents are induced in the conductor: the temperature quickly rises. As a result, the gold border simply flies off. This will not happen in an air fryer.
A microwave oven is suitable for heating food. You simply place a plate on the rotating table and take out the finished warm food. Buy a small microwave oven to provide the table with warm food in one minute. If the volume of the plate is large, it will take a maximum of 3 minutes. It will turn out faster and more efficiently than using other equipment. Make your choice of a microwave oven when its benefits become maximum.
How does a microwave oven work?
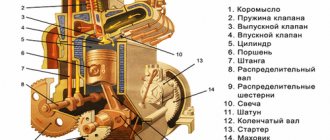
A household microwave oven consists of the following functional parts:
- a metal chamber with a metal door into which food is placed to be heated;
- magnetron - a device that emits microwave waves;
- transformer for powering the magnetron;
- control and switching circuits;
- a waveguide that transmits the radiation generated by the magnetron into the chamber.
In addition, the design of the furnace includes the following components that do not affect the heating process itself, but serve to improve the operation of the device:
- rotating stand for uniform wave exposure;
- circuit that ensures the operation of the timer;
- a safety circuit that blocks the operation of the device in various situations (for example, when the door is opened);
- a fan necessary to ventilate the stone and cool the magnetron.
How does a magnetron work?
The magnetron is the main device of a microwave oven, which emits the microwave waves necessary for heating. In fact, it is a high-frequency vacuum diode with a cylindrical copper anode. From the inner wall, this anode is divided into several sectors with copper walls.
The cathode, made in the form of a rod, forms the center of this structure (check out the picture). Thanks to the filament placed inside it, electrons are emitted. At the end sides of the device there are powerful ring-shaped magnets. With the help of the magnetic field created by them inside the magnetron, microwave radiation is generated.
During operation, a voltage of 4 kV is applied to the anode, and only 3 V to the filament. This provokes the emission of electrons, picked up by a high-tension electric field. The magnetron generation frequency is determined by the anode voltage and the geometry of the resonator chambers.
To remove energy, a special wire loop is used, running from the cathode to the emitter in the form of an antenna. From it, through the waveguide, microwave waves enter the main chamber. The output power of magnetrons installed in household microwave ovens is typically 800 watts.
To reduce the intensity of operation of the magnetron, the control circuit turns it on for short periods of time, with pauses between them. So, for example, in order for the output power of the magnetron to be 50% (400 W), it is necessary to alternately turn it on and off every 5 seconds. This control principle is called pulse width modulation.
The operation of the magnetron is accompanied by the release of a large amount of heat, therefore, to prevent overheating, it is equipped with a plate radiator, to which air is constantly supplied from a fan.
Thermal fuse
Temperature overload (overheating) is the most common cause of magnetron failure, which is why thermal fuses or thermal relays are installed on them. It is of particular importance for microwave ovens with functions that require long-term operation of the magnetron, for example, grills.
A specific device is selected based on the nominal temperature indicators that are printed on their body.
The principle of their operation is quite simple:
- The thermal relay has an aluminum housing and is installed at the location whose temperature needs to be controlled using a flange connection, providing direct thermal contact.
- The bimetallic plate located inside the fuse is pre-set to operate at a given temperature.
- As soon as the device heats up to the specified limit, the plate bends and, with the help of a pusher, breaks the connection on the contact group plates, as a result of which the power to the microwave oven is cut off.
- As the device cools, the bimetallic plate takes on its previous shape, the pusher returns to its initial position and the contact group closes again, supplying power.
The importance of the ventilator
One of the most important parts of any microwave oven is the built-in fan. Thanks to it, not only the magnetron is cooled, but also the rest of the circuit.
Using the thermostat alone to prevent microwave components from overheating is not enough. Firstly, this will lead to constant operation of the thermal fuse and the magnetron turning on and off, which will negatively affect not only it, but also other devices. Secondly, in some microwave ovens the thermostat simply cannot cope with the heat - in appliances with a grill function you cannot do without a fan.
During operation of a microwave oven, a large amount of heat is generated not only by the components included in its design, but also by the heated products. And since the main “target” of microwave waves is water, heating is also accompanied by the release of steam. The fan allows you to get rid of excess humid air by pumping fresh air into the chamber. Thanks to this, the released steam escapes through the ventilation holes to the outside.
In microwave ovens with one fan located at the back of the device, special air ducts come from it, carrying fresh air first to the magnetron and then inside the chamber.
The principle of operation of a microwave oven
In order to heat up food, you need to place the dish with food in the microwave oven and select a program; if you use quick heating, you need to set the time. Products are heated by exposure to powerful electromagnetic radiation. The frequency of microwave ovens installed in the kitchen is 2450 MHz. How food is heated: High-frequency waves penetrate deep into the food and begin to affect polar molecules (most often water), causing them to move cyclically along the electromagnetic field lines.
Thanks to the use of this method, heating of food occurs not only outside, but also inside the food. In most models used in the kitchen, this figure ranges from 2.5 to 3 centimeters.
See also:
- 5 Best LG Microwave Ovens of 2021
- 5 Best Microwave Ovens from Daewoo Electronics
- 5 Best Panasonic Microwave Ovens
- 6 Best Horizont Microwaves of 2021
- 6 Best BBK Microwave Ovens
- 6 Best Korting Microwave Ovens
Protection system
Powerful high-frequency radiation from a magnetron can cause irreparable damage to human (and not only) health, so modern models of microwave ovens pay special attention to preventing this danger.
To protect the user and other living beings from harmful radiation, microwave chambers are made of shielded metal. And since the camera itself is also placed in a metal case, there is actually two-level isolation of microwave radiation.
You may ask a completely reasonable question: is the glass door through which we observe the readiness of the dish dangerous? Isn't she a "hole" in this defense? Rest assured - the glass is covered with a special fine-mesh metal mesh that reflects radiation emitted by the magnetron with a frequency of up to 2.45 GHz (with a wavelength of up to 122 mm) back into the camera.
Of no small importance is how tightly the door closes and fits against the body. The gap between its groove and the body is specially measured at the factory (it is equal to ¼ wavelength, for example, 122/4 = 30.5 mm) and must be maintained throughout the entire service life. This distance contributes to the formation of a standing electromagnetic wave, which does not extend beyond the device due to the fact that the amplitude value at the point of contact between the body and the door is zero. Such a simple and effective radiation protection scheme is known as a microwave choke.
What happens when the door is opened?
There is an opinion that when the microwave door is opened during operation, the user is exposed to dangerous high-frequency radiation, which causes great harm to the body. In reality, this is just a myth - the magnetron control circuit includes several switches that respond to the state of the door. Their number depends on the specific model, but usually there are at least three. One is responsible for turning off the magnetron when the door is opened, the second is for the backlight, and the third transmits information to the microprocessor about the position of the door. The operation of these switches is organized in such a way that the magnetron can only operate when the microwave door is tightly closed.
How does a microwave work?
Components of a microwave oven:
- Camera. Made of metal. Equipped with a metallized door. Microwave radiation is concentrated here. This is where food is placed to be heated. Requires care.
- Magnetron. High frequency microwave emitter.
- Transformer. Magnetron power supply.
- Communications and control system.
- Waveguide. Transmits microwaves from the emitter to the chamber.
Additional details:
- Pallet. By rotating, it promotes uniform heating of the cooking objects.
- Fan. For ventilation of the chamber and cooling of the magnetron.
The operation of a microwave oven comes down to the release of energy by a magnetron, which is converted into heat. The device is connected to a transformer-stabilizer. Once this device was the most expensive in the microwave oven, today its cost has decreased and microwave ovens have become much more affordable.
The basic electrical circuit of all microwave ovens is almost the same, only their characteristics, capabilities and design are different.
What is a magnetron
Its purpose is to generate radiation of a given frequency. Essentially, this is an electric vacuum diode. Its structure:
- It has a cylindrical anode. It has a round cross-section and ten sectors with copper walls.
- In the center of the diode is the cathode. Inside it is a glowing filament. The function of the cathode is to emit electrons.
- At the edges of the magnetron there are ring-shaped magnetic elements. Their task is to create a magnetic field in the emitter. This field is a generator of high-frequency waves.
- The voltage applied to the anode is 4000 V and to the cathode filament is 3 V.
Due to the voltage difference, the cathode emits electrons, which are trapped by a high-strength electric field. The generation frequency depends on the configuration of the resonator chambers and on the anode voltage.
The energy is removed through a loop of wire, which is connected to the cathode and output to the radiating antenna. Radiation from the antenna is directed to a waveguide, through which it passes into the microwave oven.
Conventional microwave ovens use magnetrons with a power of 0.8 kW. Sometimes, to prepare a dish, you need power less than 0.8 kW, then the device turns on for short periods of time, interspersed with pauses.
This operating principle is known as pulse width modulation. Since the magnetron heats up while operating, it is placed in a plate-type radiator, which is constantly blown by a fan. Overheating may cause damage. To prevent this from happening, install a special thermal fuse.
What does a thermal fuse consist of?
These devices are also known as thermal relays. They are produced for different temperature ratings.
The thermal relay consists of an aluminum housing, which is attached to the temperature control point with a flange connection, and a bimetallic plate set to a certain temperature value. When the heating exceeds the permissible threshold, the plate, bending, triggers an element that opens the contacts - the power to the stove stops.
When the magnetron cools down, the bimetallic plate will take its original shape and the contacts will close - the furnace will turn on.
Description of fan operation
Without a fan, work is impossible. Its functions:
- Blowing air over the radiation source and other electronic circuit components that generate heat.
- If there is a grill, then the fan blows it too.
- During cooking, a lot of heat and steam are generated in the chamber. Thanks to the fan, increased pressure is created, squeezing warm air and steam through the ventilation holes.
The fan is located near the back wall of the device. Sucking air from the room, it directs the air flow through the air ducts to the magnetron plates, and then into the chamber. The fan blades are driven by an asynchronous AC motor.
How the door works
Thanks to the door lock, which is activated when the door is opened, users are protected from radiation exposure. The door structure is quite complex - the safety of the owner depends on its proper operation. The door design provides protection measures:
- Tight fit to the body. A stove with large gaps cannot be used. Radiation can exit the chamber through slits. The metal body of the device and the special groove in the door must be separated by a gap whose width is equal to ¼ of the length of the microwave. In such a gap, an electromagnetic wave of a standing type is formed, which has zero amplitude at the point where the door adjoins the body, which is why it does not go beyond the chamber. This method of protection - from waves using the waves themselves - is called a microwave choke.
- There is a high-frequency choke along the perimeter of the door, which reduces radiation to a safe level.
- When casting the door body, various additives are used, thanks to which the metal absorbs radiation better. They do not provide 100% absorption, but the weakened waves definitely do not pose a danger to humans.
- To prevent the stove from turning on when the door is open, the device has a system of switches that control its position. As a rule, there are three switches - to turn off the magnetron, to turn on the backlight, and to transmit a signal to the control unit. The setting and location of the microswitches does not allow them to operate when the door is open.
Protection system
Every microwave is a source of powerful radiation that can cause great damage to the human body and all living things. To protect others from exposure, the device is shielded with a metal casing, through which high-frequency radiation cannot pass.
The door is equipped with transparent glass so that the user can observe the processes of heating, cooking, and defrosting. The glass is also shielded - it has a fine-mesh metal mesh on it, which prevents the penetration of microwaves.
Control unit design
Tasks of the control unit - the “brain” of the microwave oven:
- Maintain the specified power.
- Turn off the oven at the end of the process.
In early versions, control was carried out by two mechanical switches: one set the power, the other set the time. Today, devices are equipped with electronic and microprocessor control units that control, in addition to the two mentioned, many functions - important and unimportant. For example:
- built-in clock;
- sound signal about the end of the process;
- power display;
- cooking dishes according to special programs “built into” the unit’s memory.
Control block
The control unit plays the most important role in the operation of any microwave oven. In fact, it is the brain of the furnace, performing two basic functions:
- maintains the power value at a given level;
- stops operation of the device after a specified period of time has elapsed.
The control unit circuit of older models was a design of two switches, one of which served to set the timer, and the other to select the processing intensity. As technology developed, the “filling” of microwaves also improved - electromechanical control units were replaced by electronic ones, which today have already been replaced by microprocessor ones. Their advantage lies not only in compactness, but also in broader functionality, including:
- power setting using touch or push-button keyboard;
- display of current power on the display;
- built-in clock;
- numerous presets for preparing various dishes and performing specific tasks (several defrosting modes for different types of products);
- automatic calculations - for example, you enter only the weight of the piece of meat to be defrosted, and the oven itself selects the power for it;
- a large selection of sound signals for completing the work cycle.
A separate power supply is used to power the control circuit. A relay unit is used to transmit signals and commands between the unit, keyboard, magnetron, grill, lamp and fan. To connect other components (display, keyboard) to the circuit, cables are used.
Inverter technology
When choosing a microwave oven, many consumers try to find a model with a large chamber volume to ensure maximum versatility. Unfortunately, functional elements often occupy most of the total volume of the device; accordingly, the size of the oven is large, but its useful volume is small. This problem was one of the main ones before the advent of inverter furnaces.
This technology can significantly reduce the space occupied by the magnetron through the use of smaller components. This allows you to create larger chambers while keeping the dimensions of the entire microwave within accepted standards.
Inverter technology is fundamentally distinguished by the fact that in such microwave ovens the emitter does not have to constantly operate at maximum power, unlike classic magnetrons. The intensity of processing is regulated by pulses, so that the food is not exposed to powerful surges of microwave energy, which affects its quality. Studies have confirmed that cabbage processed in an inverter microwave retains one third more vitamin C, and pork retains 41% more vitamin B1.
In addition to being compact and useful, inverter microwave ovens are also more economical devices, thanks to the use of only the amount of electricity that is necessary to maintain the selected power. Fine pulse adjustment of the operating mode also serves to speed up the defrosting of food.
Today, the flagship company in the application of this technology is Panasonic, which released the first inverter microwave oven.
Myths about microwave radiation
There are several well-established misconceptions about the harmfulness and danger of using microwave ovens. In fact, most (usually all) are wrong. Listed below are common myths about microwave ovens that are actually not worth your trouble.
- A microwave can electrically damage appliances located a few meters away from it if left on for a long time. In fact, modern microwave ovens are completely protected from radiation escaping outside the chamber. The minimum radiation, which may be in the immediate vicinity of the device, does not exceed the radiation of a computer system unit.
- Microwave ovens may cause the user to become allergic to electromagnetic waves. This is simply impossible. There are only a few people in the world with such a rare disease and its causes are in no way related to the use of microwaves. In general, no household appliance creates such dangerous radiation, since all models undergo safety certification.
- Products become radioactive when exposed to microwave waves. This is also incorrect. Microwave microwave radiation is non-ionizing and therefore does not change the properties of food. The statement about the carcinogenicity of products exposed to microwave processing is also incorrect - microwaves have a completely different operating principle than X-rays and, once again, cannot in any way affect the properties of products.
- Microwaves pose a high health hazard. This has already been partially said - direct exposure to microwave radiation is indeed detrimental to tissues, but if you follow the rules for using a microwave, you will never be exposed to such effects. In fact, radiation from a microwave oven represents only a small fraction of the total electromagnetic field in which we find ourselves while using numerous other household appliances.
Just remember that the oven door must close tightly and the body must be intact, and also do not touch the operating microwave with your hands or other parts of the body and you can rest assured that at a distance of half a meter from the device you are exposed to no more electromagnetic radiation than when watching TV.
How does a microwave oven work?
The device operates on the basis of electromagnetic waves. Electromagnetic energy allows you to influence objects and heat them. The waves themselves can be from a millimeter to one meter, and can also reach the speed of light. Not only a microwave oven, but also satellite communications, the Internet or television operate using this radiation. Now you know what kind of radiation a microwave oven produces.
The device has a part responsible for converting the electromagnetic field into a microwave field. It's called a magnetron. This type of energy interacts with food molecules and thus creates an increase in temperature.
Sometimes microwave radiation measurements can be made by testing such food. By studying its structure and composition, one can say a lot about what kind of exposure the product was exposed to and how safe it is for humans. When foods are heated in a microwave oven, the molecules of these foods are exposed. At the same time, there is an opinion among scientists that during the deformation of molecules, the genetic structure of products of animal and plant origin also changes. And this, in turn, can be fraught with consequences for the person who eats such products.
But that is not all. The radiation that comes from the magnetron also affects the liquid. Therefore, the harm from microwave radiation can be very serious. The liquid is found in many foods that humans consume. This radiation in the liquid is converted into thermal energy. The thermal effect on the products is only a few centimeters from the outside and therefore the product is not heated from the inside.