Additive technologies have been reaching the masses for a long time: institutes and research centers have been closely working on them since the 80s, and now the moment has come when you can touch high-tech and master 3D printing right at home. You don’t even have to break the bank to do this: prices for 3D printers are on par with average smartphones. Let's figure out how it works and what opportunities open up for makers and DIY enthusiasts!
Everything for 3D printing ❯
Why do you need a 3D printer?
The printer will be very useful for DIY engineers. You no longer have to look for a universal housing for your project and then drill additional holes in it. 30 minutes of design, a few hours of printing - and you already have a ready-made case that is ideal for your device. Does an assembly of 5 shields fit anywhere? Forget about such problems.
The printer will definitely help in repairing things around the house. Everyone has had a situation in their life when they had to throw away something even though only one plastic part was broken. With the help of 3D printing, you can easily replace rare plastic parts in devices that are difficult to find separately.
Until you learn how to model plastic parts yourself, you can simply download them on the Internet. There are many sites with millions of ready-made free models that users freely share. We have dedicated a separate article to searching for models.
What are the types of 3D printers?
There are several main types of 3D printers, which differ radically in their operating principles.
FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) technology
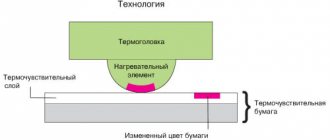
The most common type is FDM printers with layer-by-layer deposition of plastic. They work due to a movable print head with a heating element. Plastic is fed into it in the form of a rod, which melts and is squeezed out in liquid form onto the printing table. In this case, the plastic is blown by a fan and instantly hardens, and the head begins to squeeze out a new layer on top of the hardened one.
SLA technology (Stereolithography Apparatus)
SLA printers work on the basis of stereolithography: instead of plastic, a special photopolymer resin is used, which hardens under the influence of ultraviolet rays. To print, resin is filled into a vat, at the bottom of which there is a display with ultraviolet pixels. A drawing of the bottom layer of the model is displayed on it within a few seconds. In this case, the resin above the display hardens into the displayed pattern and then sticks to a special movable table on top. After this, the table with the first layer is raised, and polymerization of the next layer occurs in the resin.
SLS (Selective Laser Sintering) technology
SLS printers use selective laser sintering technology, which uses special plastic powder. During the printing process, a thin layer of powder is poured in and the printer lasers it to harden the layer to match the model. Next, the next layer of powder is poured and fused with the previous one - and so on in a circle. In the end, all that remains is to clean the finished part from any remaining powder, which can then be reused.
Technology comparison
Each type of 3D printer has its own advantages and disadvantages.
- SLS printers are large and require expensive raw materials. They are often used in high-tech production for one-piece parts.
- SLA printers are much more widespread. An ultraviolet display improves accuracy, but working with toxic photopolymer resin at home is difficult.
- FDM printers are the most popular among hobbyists. A plastic rod is much cheaper than a special powder or photopolymer resin. However, to print complex geometry on such a printer, you will have to take care of auxiliary supports. And the printing speed is on average lower than with other technologies. But FDM printers are the easiest and safest to maintain.
How to choose a 3D printer
When choosing a printer, first of all you need to decide what technology is used for printing. An amateur-level device, and only one that can potentially be purchased by the average consumer, and not an entire enterprise, operates on the basis of a development called Plastic Jet (PJP), in some sources it is referred to as Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) or Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF) . Essentially it's the same thing.
Types of materials for amateur printing
Basically, for printing on devices of this type, plastic with different characteristics is used. It is packaged in the form of a plastic cord wound on a reel or cut into strips. Two types of plastic are widely used: ABS and PLA.
ABS plastic is safe, non-toxic, suitable for children's products, moreover, it can be worked with in the presence of children. Products made from it are durable and last a long time. The disadvantage of plastic is that it loses its presentation in the sun and in severe frost. It is more often used in professional parts manufacturing.
PLA plastic (polylactide) is more fragile and does not serve as well. But it is more flexible and provides more opportunities for complex shapes. It is a natural product as it is made from corn and sugar cane. It is environmentally friendly when disposed of and decomposes 100% into safe components. Products made from PLA are resistant to abrasion and maintain their geometry. Therefore, plastic is great for moving parts. In general, this is more of an amateur version of plastic.
Alternative materials for 3D printing
In addition to plastic, the following materials are used to operate such printers.
- Stainless steel. Used only in professional equipment. Provides great opportunities for manufacturing parts.
- Tree. In fact, it is not wood, but a mixture of a binding polymer with a wood additive. This material is very expensive and does not require any special skills. Products made from it are “warm” and cannot be distinguished from wood in appearance.
- Resin is also expensive. It can be used to print high-precision parts with excellent surface quality - smooth and durable. When exposed to the sun, the resin loses its transparency.
- Nylon. It is mainly used for the manufacture of elements for industrial and medical purposes.
Important! When purchasing printing material, please note that the spool format and cord thickness must match the operating characteristics of the printer.
Characteristics of 3D printers
To choose a printer or conduct an analysis to identify a leader, you need to understand what device characteristics are key.
- Print area. This parameter determines the maximum volume of parts that can be created using this equipment. The documentation indicates either the volume in cubic cm or the maximum linear dimensions in mm.
- Print resolution (layer). This is the thickness of the layer with which the material is applied. The higher the resolution, the thinner the plastic is applied, the reliefs are calm, and the surface is of high quality. Below this value, the details come out more “clumsy”, without fine elaboration. In some devices this parameter can be set by the operator.
- Extruder. This is the working unit of the printer, which is responsible for preparing (heating) and dispensing the material. The plastic (or other raw material) is softened by high temperatures in the nozzle and fed to printing (extruded). This unit includes the nozzle itself, a conveyor for the cord (plastic thread), a temperature controller and a cooling mechanism. 3D printers with one extruder can only use one filament per pass. To make multi-color sadness possible, the device must have at least 2-3 extruders. In industrial devices, a single unit with a double nozzle is possible. This is expensive, and household devices are not equipped this way.
3D printer with two extruders
- Printers can “connect” to external devices (computer, smartphone, or just external memory) via USB and/or Wi-Fi. This is not always a prerequisite for work.
- Printer firmware (software). By default it is preinstalled. His responsibilities include recognition and processing of documents in stl format for subsequent printing. These files are created in professional programs such as Sketchup and Autodesk Inventors Fusion.
- Additional functions. Ergonomics, design and other details do not interfere with the workflow of the printer, but often determine its cost.
3D printers can be supplied as an independent device (Assembled) or in the format of a designer, when the user assembles it himself (DIY). The second option costs significantly less.
How to prepare a seal
The process from the birth of an idea to the release of a finished plastic part is not difficult - a student can handle it. We've broken it all down in our 3D printing guide using the Flying Bear Ghost 5 printer as an example, and here we'll show you the general principle.
Original model
First you need to create or download a 3D model of the future part. As a rule, sources are stored in STL format, which describes the polygonal structure of the model in the form of many triangles. But you won’t be able to immediately send such a file to the printer: for successful printing, you first need to break the detailed 3D model into layers that the printer can handle.
Slicing
The program for slicing models (slicer) will require very little from you - enter the model of your printer and set the printing settings: layer thickness, percentage of internal filling of the part, auxiliary supports, and the like. Based on this data, the slicer will automatically prepare a special code for the printer - G-Code, which describes how to move the print head, to what temperature it should be heated and at what speed to extrude the plastic in order to obtain the desired model layer by layer. Then all that remains is to load this code into the 3D printer and be patient until the end of printing.
The entire process of preparing a model is clearly illustrated by the program and is provided with intuitive tips for novice users. In general, slicing is not as scary as it is made out to be!
Treatment
After the model is ready, it can be further processed with sandpaper or a chemical solution. This will smooth out any unevenness between layers and the piece will look exactly like the factory one. There are many life hacks on the Internet that will help minimize the flaws of the model and give it an improved look.
Printing consumables
The properties of a printed item largely depend on the raw material. As we have already said, FDM 3D printers use plastic filaments as consumables, and you have a huge scope for experimenting with different types of plastic.
- PLA plastic lends itself well to extrusion and allows you to print complex shapes at relatively low head operating temperatures of 190 °C. The biodegradability of PLA plays into the hands of the environment, but at the same time, things made from it are not very durable.
- PETG plastic is stronger than PLA, but is also well suited for printers with temperatures around 200 °C. Varieties of PET plastic are familiar to you from bags and plastic soda bottles.
- ABS plastic has higher strength compared to other types. However, for high-quality printing from ABS plastic, your printer will need an increased extrusion temperature of about 250 °C and a table heated to 120 °C, so not every model can support it.
- HIPS plastic is similar in temperature properties to ABS, but has low agglomeration with it and is easily removed with an organic solvent. Because of this, HIPS plastic is often used to print composite models and supports for ABS models.
- Wood plastic is made with the addition of wood dust. Finished models made from it do a good job of imitating wood not only in their appearance, but also in their smell.
Plastic spools are found on sale at every step - it will not be difficult for you to choose suitable consumables and combine different properties and colors of parts when printing.
FDM or FFF
FDM (fused deposition modeling) technology involves printing using a dispenser nozzle, from which any material is extruded and gradually applied to the object layer by layer, building a three-dimensional model. The materials for this type of 3D printing are most often plastics (in the form of threads on a reel), but not only. For example, FDM printers can be used as a culinary assistant (in this case, icing, cheese, dough, and other components necessary for a dish are refilled) or an FDM printer can be used in medicine (in this case, a special medical gel with a set of living cells is refilled - usually , used in biomedicine). FDM printing technology was developed by S. Scott Trump back in the late 80s of the last century and entered the market in 1990. Another name for this printing technology is FFF (Fused Filament Fabrication), or Fused Filament Fabrication, and it was coined to circumvent the legal restrictions on the FDM acronym, which is owned by Stratasys. This type of 3D printer is most common as a household 3D printer, as it is the least expensive to maintain. In manufacturing, FDM printers are most often used for rapid prototyping or rapid modeling of objects, for example, a small-scale batch of any parts. In everyday life, such printers can be used for a variety of purposes, for example, for printing toys, souvenirs or decorations.