History of origin
The ancestor of inkjet printers is a device for recording received messages from telegraphs, which was invented by William Thomson in 1867. The operating principle was based on the control of falling drops of dye onto a paper medium by electrostatic laws.
Based on this technology, in the middle of the last century, engineers developed a device for recording information on paper. The device had a number of disadvantages, including a high price, poor image reproduction quality, and paper getting dirty. But for seismographs, electrocardiographs, and multimeters, this quality was sufficient.
Over time, inkjet printing began to use piezoelectric laws and crystals, which, when electricity passed through them, could change shape and emit electrons. Canon then developed another method for displacing ink onto the media. They began to be exposed to temperatures of up to 400 °C, because of this the ink changed from a liquid state to a vapor state and was sprayed onto the paper.
HP specialists were the first to invent a color device. Three dyes were used in printing: blue, yellow and purple, mixing which you could get any shade.
A little history
William Thomson can be considered the indirect inventor of this type of printer. But his product was not a “streamer” as such, but was intended to record the reception of messages from telegraphs. But the principle of printing was to apply electrostatic laws to “control” the falling drops of ink onto the paper. This was a long time ago - in 1867.
This technology was revived already in the middle of the last century with the easy help of engineers. Their inventions were used in various devices for recording data on paper. But they also had significant disadvantages: high price, poor quality of the reproduced picture.
Soon, piezoelectric laws and crystals were used in inkjet printing. All this became possible due to the ability of the latter, under a certain influence, to “emit” electrons, and when a current passes, change their shape. Later, Canon came up with another way to “squeeze” paint out of ink tanks. The liquid came out in the form of steam under the influence of high temperature.
The first inventors of color inkjet printing were specialists from HP. Any shade was “prepared” by mixing three color paints: blue, red, yellow.
Inkjet printer device
Printhead
A separate part consisting of many small nozzles. The design of the print head is practically the same for different printers. Only the number of holes and their location can change. So, in the first models there were only 12 of them, but now it can reach several thousand. Ink is extruded through nozzles using piezoelectric or thermal technology.
Characteristics of PG:
- Number of flowers. The minimum is 4, the maximum is 12. The more dyes, the better the quality of the print and the better the color rendition.
- Drop size. The smaller the drop of ink that is squeezed out, the clearer the drawing.
- Print resolution. The more dots fit on one inch of sheet area, the better the image.
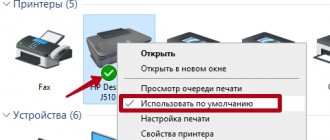
In some printers, the PG is not a separate element, but part of the cartridge (Fig. 1).
Rice. 1
Rice. 2 - cartridge without built-in head
Cartridge
This is a small plastic container no more than 10 cm long. Black dye is stored in a separate container, and colored dye can be in both separate and combined cartridges. The combined inkwell looks like a plastic box, which is internally divided into three compartments by partitions.
Rice. 3
Rice. 4
Paper feed mechanisms
It includes a paper tray and a motor that drives the feed rollers. The tray for different models can be located either at the top or at the bottom. The main problem with the mechanism is the failure to capture pages, but this is rare and can be easily fixed on your own.
Control Panel
May consist of just a few buttons or have a built-in screen to control settings. The panel is intuitively easy to operate and may additionally have explanatory notes. Located on the front of the printer.
Rice. 5
Frame
This is the outer shell made of black or white plastic. Protects the working mechanism from contamination, moisture and sunlight. The housing of an MFP and a regular printer may differ.
Motors
There are only four of them:
- Responsible for the operation of the roller, which grabs the page and draws it inside the printer.
- Activates the automatic feeder.
- Activates the mechanism that moves the print head.
- Helps deliver ink from the cartridge to the paper.
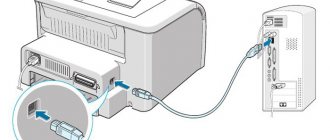
Connectors
LTP cables have been replaced by USB and Ethernet. They are easier to use and faster. If the equipment is old and has an LTP port, the connection to the computer can be done via an adapter.
Sensors
There are optical and mechanical.
Perform the following functions:
- determine whether the page has entered the machine;
- monitor the position of the head in relation to the sheet;
- monitor paper size and characteristics;
- detect the presence of foreign objects inside the printer.
Rice. 6
Working principle of an inkjet printer
The principle of operation of an inkjet printer is that the ink is applied to sheets of paper in droplet form through special nozzles. The size of each droplet is very small and they arrive by extrusion.
Depending on the manufacturer, this equipment can print using several technologies:
- Drop -on-demand. A specially built-in mechanism in tandem with a heating element sprays ink on demand so quickly that print quality and speed are significantly improved. During color printing, more contrast and clear image details are obtained. This method is great for printing graphs and diagrams - they have clear lines.
- Thermal method. Each nozzle has a built-in element that has the property of heating to a very high temperature when an electric current passes through it. This action promotes the formation of gas bubbles, which displace the ink onto the paper in the required quantity. After turning off the current, the heating element cools down and produces a new portion of ink. The service life of printers operating using this method exceeds the service life of other devices operating using other methods. The disadvantage of this method is that during continuous filling, the image looks blurry.
- Piezoelectric method. This method consists in the fact that each nozzle has its own flat-shaped piezoelectric crystal, which is connected directly to the diaphragm. When interacting with an electric field, it is deformed, that is, it first contracts and then expands, filling the system with ink. Thus, dots remain on the paper, which make up the entire image.
Continuous feed differs from demand feed in that the delivery of dye depends on the modulator.
The difference between cartridges and CISS
Typically, inkjet cartridges can be refilled with a medical syringe and pre-purchased ink.
If the ink cartridge is a plastic can with two holes in the body for refilling ink and creating internal pressure, such a cartridge is called “refillable” or “refillable (REC)”.
It has a number of disadvantages:
- Refueling needs to be done frequently, which is not always convenient at home.
- Additional tool required.
- To determine the amount of ink, the cartridge must be removed from the printer each time.
- If the cartridge is opaque, you can only find out the level of remaining dye using software.
- Do not allow the ink level to drop below the manufacturer's recommended value to prevent overheating of the nozzles or the formation of an air lock in the head.
- Due to frequent removal, the cartridge wears out quickly.
A continuous ink supply system helps eliminate these disadvantages. It consists of four or more transparent containers and a set of thin tubes (loops). They hold from 80 to 100 ml of ink, which is much more than the volume of conventional cartridges. If you work in medium-intensive mode, you will rarely have to add paint to the CISS. The refueling process is simple. CISS is more expensive than conventional ink tanks, but using such a system during intensive work is much more profitable.
Rice. 7
Disadvantages of CISS:
- Additional space needed. If the CISS is not included in the factory package, there should be additional space for the system near the printer.
- Poor maneuverability. Moving a printer with CISS even over very short distances can lead to settings failure.
- Photophobia. Containers with dye must be protected from direct rays of the sun, the impact of which negatively affects color rendering.
Inkjet printers
There are three types of inkjet printers: document printers, photo printers and MFPs. They all print using the same technology: liquid ink from a cartridge is applied to paper in the form of tiny dots, from which an image is formed.
The inkjet MFP prints color images very well.
- Printers for documents are the cheapest, their cost rarely exceeds 6 thousand rubles. They work best when printing text documents. It can be either black and white or color.
- Photo printers are slightly more expensive and are aimed at high-quality color printing of small photos (up to 8x10 in size). As a rule, this is enough for home printing or a small photography business.
- Multifunctional devices (MFPs) at a relatively low price combine the functionality of a printer, scanner, copier, and sometimes fax.
The advantages of inkjet printers include the following:
- Small size . Most inkjet printers are relatively small and can fit into tight spaces. MFPs are slightly larger, but they are generally smaller than a laser printer and much smaller than a standard office copier.
- Low cost . Inkjet printers, in general, are much less expensive than laser printers. If an inkjet printer breaks down, it is much easier to replace it with a new one.
- Inexpensive consumables . Inkjet printer cartridges have become cheaper in recent years. An ink cartridge costs about half as much as a laser toner cartridge. In addition, it is easier to replace.
- Excellent photo printing quality . Inkjet printers designed for photo printing can produce stunning results, producing images with vibrant colors and high contrast with virtually no pixelation.
Inkjet printer: inside view.
Among the disadvantages of inkjet printing are the following:
- Wasteful ink consumption . To print one page, an inkjet printer requires much more consumables than a laser printer.
- Slow printing . An inkjet printer can print multi-page documents much more slowly than a laser printer.
- Problems with the cartridge . At times, ink cartridges can leak, causing the printer, hands, and paper to get dirty. In addition, ink cartridges tend to dry out if not used regularly.
Overall, an inkjet printer is a popular consumer choice for home use. Buy an inkjet printer if you:
- choosing a printer for your home;
- want to print photos;
- intend to print small documents frequently;
- limited in funds.
How does an inkjet printer work?
- Pulling rollers pull the paper into the machine.
- Ink is supplied to the print head. They are mixed in a certain proportion to obtain the required shade, and then squeezed out through nozzles onto a piece of paper.
- The image coordinates and the applied color code are transmitted to the head. The motor activates the drive belt, which moves the head along specified coordinates.
- After mixing, the dye is released onto the paper through fine nozzles. The output method will depend on the printing principle (thermal inkjet or piezoelectric printing). The first option is suitable for water-based inks, the second - for pigment inks.
- Color ink is sprayed onto paper at a speed of 20-25, black ink - more than 35 thousand drops/s. You can print 10 or more pages per minute.
Image application methods
Piezoelectric
The method is based on the ability of flat piezocrystals connected to a diaphragm to change their shape under the influence of electricity passing through them. By compressing and unclenching, the crystals cause the ink to come out of the head and form a pattern on the paper consisting of small dots. The method is used by Epson and Brother.
Rice. 8
Gas bubble method
The method is called Bubblejet. For printing, nozzles (nozzles) are equipped with special elements that become very hot under the influence of electricity. After heating, the liquid paint turns into gas bubbles, increasing in volume and increasing the pressure under which excess dye comes out. The technology is actively used by Canon.
Rice. 9
Rice. 10
Printers using this technology are more reliable, draw lines better, but areas of solid infill appear blurry. The method is suitable for printing graphs and diagrams that require high precision lines.
Drop-on-demand method
The technique involves a separate mechanism that works in conjunction with a heater. It quickly and accurately applies paint to the right places on the sheet, providing high contrast and color saturation. This printer can be used to print halftone graphics.
Creating different shades
All shades are created with three colors of ink - cyan, magenta and yellow. They are mixed in the right proportions to obtain the desired shade. Black paint comes from a separate container. For better quality prints, modern models use more than four colors.
Delivery on demand
Employees from Siemens, Canon, and HP have been developing technology for several years to make the printer not so complicated and large. The problem they wanted to solve was to allow a drop of ink to flow through the nozzle only when it was actually needed. All three teams were successful.
Siemens was the first to introduce its PT-80 printer in 1977. According to the developed technology, ink droplets fell onto the paper at the right time using piezoelectronic tubes. Two years later, Canon completed the development of a method for heating the dye with thermal elements and called it BubbleJet, or the gas bubble method. Almost simultaneously, HP completed the project and used the same principle in its research. But the technology is somewhat different and, naturally, the team came up with a different name: drop-on-demand.
BubbleJet
Bubble Seal
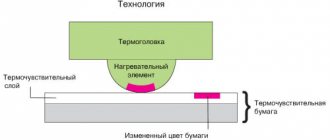
The method is based on the use of thermal elements that heat up to 500 °C when an electric current passes through them. The ink boils, and the resulting gas bubble squeezes a drop of ink through the nozzle. After heating stops, the bubble drops and a new portion of dye enters the chamber.
The high quality of printing text, lines, histograms, but a somewhat blurry graphic image in the area of solid filling, is explained by the presence of splashes escaping from the nozzle accompanying the main drop of ink. The thermal principle of operation of an inkjet printer imposes certain requirements on the composition of the ink:
- compatibility with the materials from which other parts of the print head are made;
- an aqueous base that allows gas bubbles to form;
- the ability to withstand heating temperatures and not delaminate, not leave soot, and not ignite.
Drop-on-demand
The heating element is located directly opposite the nozzle, gas bubbles move in the same direction with the ink, and do not squeeze the dye to the side, as with the BubbleJet method.
Drop-on-demand method
This is not the only difference. The thermal element here is heated to a temperature of 650° C, which causes the ink to boil and escape through the nozzle in a gaseous state. These vapor clouds make printing clearer in the solid fill area, which is a clear advantage over gas bubble technology.
A significant drawback of both methods: the print head quickly fails as a result of constant exposure of the parts to high temperatures. The size and cost of the heating system are small, which allowed manufacturers to combine GHG and cartridge. Consumers are asked to throw away the consumables when they run out of ink.
Many users refill cartridges themselves or install CISS, but one cannot expect much durability of the head precisely because of the printing method. It is especially important for owners of thermal inkjet printers produced by Canon, HP, Lexmark to monitor their ink levels. It is the dye that acts as a coolant, and when printing with an empty cartridge, the PG will most likely fail beyond repair.
What ink is used
- Water soluble (Fig. 11). They print bright pictures, images and photos. They have no solid components. They have a short shelf life. Over time, the image fades and loses saturation, especially under the influence of the sun. The paint is afraid of water and high air humidity.
- Pigment (Fig. 12). The composition contains solid particles. They are less susceptible to the effects of water, moisture and sun. Printed images remain high quality for more than 70 years, but the photos are less saturated and the real tones are poorly displayed. Paint should not be applied to glossy paper.
- Sublimation (Fig. 13). The dye is similar to pigment ink, but is intended for printing not on paper, but on synthetic fabrics. In addition to ink, thermal transfer paper is needed for printing. The pattern is fixed under high temperature. To save consumables, it is better to use CISS.
Rice. eleven
Rice. 12
Rice. 13
Inkjet printers. The operating principle of inkjet printers is similar to needle printers
The operating principle of inkjet printers is similar to needle printers. nozzles are used here , which are located in the printer head. This head contains a reservoir of liquid ink, which is transferred through nozzles as microparticles to the media material. The number of nozzles ranges from 16 to 64, and sometimes up to several hundred.
There are two methods used to store ink:
− the printer head is combined with an ink reservoir; replacing the ink tank is simultaneously associated with replacing the head;
− a separate reservoir is used, which supplies the printer heads with ink through a system of capillaries.
The operating principle of inkjet printers is based on:
− piezoelectric method;
− gas bubble method.
To implement the piezoelectric method, a flat piezoelectric crystal connected to a diaphragm is installed in each nozzle. Under the influence of electric current, the piezoelectric element is deformed. When printing, a piezoelectric element located in the tube, squeezing and unclenching the tube, fills the capillary system with ink. Ink that is squeezed back flows back into the reservoir, and ink that is squeezed out creates dots on the paper. Inkjet printers using this technology are produced by Epson, Brother, etc.
The gas bubble method is based on thermal technology. Each nozzle is equipped with a heating element, which, when current is passed through it, heats up to a temperature of about 500 degrees in a few microseconds. Gas bubbles that arise during sudden heating try to push a portion (drop) of liquid ink through the nozzle outlet, which is transferred to the paper. When the current is turned off, the heating element cools down, the steam bubble decreases, and a new portion of ink flows through the inlet. This technology is used in products from Hewlett-Packard and Canon.
Color inkjet printers have higher print quality than pin-type color printers and are less expensive than laser printers. A color image is obtained by using (overlapping) four primary colors. The noise level of inkjet printers is much lower than that of needle printers, since its source is only the motor that controls the movement of the print head. When printing drafts, the speed of an inkjet printer is much higher than that of a pin printer. When printing with LQ quality, the speed is 3-4 (up to 10) pages per minute. The quality of printing depends on the number of nozzles in the print head - the more there are, the higher the quality. The quality and thickness of the paper is of great importance. Special paper is available for inkjet printers, but you can print on regular paper with a density of 60 to 135 g/m2. Some models use heated paper to dry the ink quickly. The resolution of inkjet printers when printing graphics ranges from 300*300 to 720*720 dpi.
Characteristics
- Picture quality. When choosing a technology, you need to pay attention to the number of nozzles and the supported resolution. The higher the indicators, the clearer and brighter the print will be.
- Paper type. It is better when the printer can print on sheets of different thicknesses, having both a matte and glossy finish.
- Print speed. You shouldn’t get hung up on this parameter, because at high speeds the inkjet operates, the picture quality is lost. For high-speed printing, a laser printer is better.
- Noisy. Modern household models produce no more than 40 dB, industrial printers can produce a louder sound, but they are also less noisy in comparison with older models.
The operating principle of inkjet printers is based on:
- piezoelectric method;
- gas bubble method.
To implement the piezoelectric method,
a flat piezoelectric crystal connected to a diaphragm is installed in each nozzle. Under the influence of electric current, the piezoelectric element is deformed. When printing, a piezoelectric element located in the tube, squeezing and unclenching the tube, fills the capillary system with ink. Ink that is squeezed back flows back into the reservoir, and ink that is squeezed out creates dots on the paper. Inkjet printers using this technology are produced by Epson, Brother, etc.
Gas bubble method
based on thermal technology. Each nozzle is equipped with a heating element, which, when current is passed through it, heats up to a temperature of about 500 degrees in a few microseconds. Gas bubbles that arise during sudden heating try to push a portion (drop) of liquid ink through the nozzle outlet, which is transferred to the paper. When the current is turned off, the heating element cools down, the steam bubble decreases, and a new portion of ink flows through the inlet. This technology is used in products from Hewlett-Packard and Canon.
Color inkjet printers have higher print quality than pin-type color printers and are less expensive than laser printers. Color image
is obtained by using (overlapping) four primary colors.
The noise level of inkjet printers is much lower than that of needle printers, since its source is only the motor that controls the movement of the print head. When printing drafts, the speed of an inkjet printer is much higher than that of a pin printer. When printing with LQ quality, the speed is 3-4 (up to 10) pages per minute. The quality of printing depends on the number of nozzles in the print head
- the more there are, the higher the quality.
The quality and thickness of the paper is of great importance.
Special paper is available for inkjet printers, but you can print on regular paper with a density of 60 to 135 g/m2. Some models use heated paper to dry the ink quickly. The resolution of inkjet printers when printing graphics ranges from 300*300 to 720*720 dpi.
Paper feeding method
Paper can be loaded into the printer vertically from the top paper tray. When the tray is placed at the bottom, pages are printed horizontally. The sheet is picked up with a roller with a rubber pad; for more reliable fixation of the paper, an additional rubber roller is provided. Regardless of the sheet feeding method, the orientation of the printed image can be portrait or landscape; it is set in the print settings.
To ensure trouble-free page feeding, you need to keep the tray clean. No foreign objects should get into it, otherwise the sheets will wrinkle, get dirty with paint, and be picked up unevenly.
5 / 5 ( 1 voice )
Paper feed mechanism
Paper can be loaded into the printer vertically or horizontally. Vertical loading is carried out from open trays located at the top of the printer, and the orientation of the sheet during loading can be either portrait or landscape. Horizontal loading is carried out from trays, which are accessible from the front panel of the device.
| Epson Stylus Photo T50 Vertical Book Loading Paper Printer | Brother MFC-J2510 MFP with vertical landscape paper loading |
| HP Officejet Pro 8000 Enterprise Printer with Tray Closed | |
After receiving a job, the printer grabs the top sheet of paper and feeds it into the print path. A sheet of paper moves along the printing path thanks to a special mechanism, the basis of which is a roller with a rubberized surface driven by a stepper motor. The paper is pressed against the roller by additional rollers with a rubberized surface.
Some printers use duplex printing devices that allow you to automatically print on both sides of a sheet at once.
How does an inkjet printer work?
Published 09/10/2011
The inkjet printer is a further development of the idea of a dot matrix printer, so its design retains many of the elements of its predecessor.
The main element of an inkjet printer is the print head. The print head consists of a large number of nozzles to which ink is supplied. Ink is supplied to the nozzles due to capillary properties and is kept from flowing out due to the forces of surface tension of the liquid. The head has a special mechanism built into it that allows you to eject a microscopic drop of ink from the nozzle. Depending on the design of this mechanism, the printer belongs to one class or another.
Inkjet printers use one of two methods of ejecting ink droplets (also called print type):
Piezoelectric (Epson)
Piezoelectric technology is based on the ability of a piezoelectric element to deform under the influence of an electric field. Each print head nozzle has a flat membrane made of piezocrystal built into it. Under the influence of an electrical impulse, the membrane is deformed, and the pressure created by this ejects a microscopic drop of ink from the nozzle.
Gas bubble method (Canon, HP)
The gas bubble method is based on rapidly heating a small volume to boiling point. The heating rate is so high that it is similar to an explosive process. The resulting steam ejects a microscopic drop of ink from the nozzle. To implement this method, a microscopic heating element is built into each nozzle.
Each of these two methods is attractive in its own way, but each of them is not free from disadvantages.
Piezoelectric technology is the cheapest and has higher reliability (since high temperatures are not used). This control method is less inertial than heating, which allows for increased printing speed.
Bubble technology involves high temperature. At high temperatures, the heater becomes covered with a layer of soot over time, so in printers using this technology, the print head quite often fails. In such cases, it, together with the ink reservoir, forms a structural single unit.
Print heads can be structurally combined with an ink cartridge and replaced simultaneously with it, or they can be permanently installed in the printer - in this case, only the cartridge is replaced. Each of these options has its own advantages and disadvantages. It would seem that an ink tank without a print head should cost much less than in combination with a print head. In reality, this does not happen and there is no noticeable reduction in operating costs when the print head is permanently installed in the printer. At the same time, an easily replaceable print head makes it easy to overcome difficulties associated with ink drying in its channels. It should be remembered that if the ink dries in the head, it will usually need to be replaced unless appropriate action is taken in a timely manner. In order to reduce the risk of ink drying in the head channels, a special parking position is provided. Most printers have a nozzle cleaning feature. However, all this does not give complete confidence that the print head will not have to be changed during operation.
The head, together with ink containers, is fixed on a carriage, which, along a special guide, makes a reciprocating movement across a sheet of paper. Although the method of “combining the print head and ink tank is structurally the simplest and therefore has become the most widely used, it is not optimal. The fact is that the carriage must move quickly enough, and also change the direction of movement quickly enough, because the speed of its movement determines the printing speed. To do this, the movable carriage must have little inertia, i.e., have as little mass as possible. For this purpose, the volume of the ink container is reduced. Therefore, it is preferable to place the ink tank on a stationary part of the printer, and supply ink to the print heads using special pipelines.
This system makes it possible to increase printing speed and at the same time increase ink capacity, but the piping system is structurally so complex that this design is very rarely used.
During the printing process, a sheet of paper moves along the printing path using a special mechanism. Its basis is a rubberized roller driven by a stepper motor. The paper is pressed to the roller by auxiliary rubberized rollers. Broaching occurs due to friction forces when the roller rotates. In older printer designs, printing paper was fed into the printer sheet by sheet. This was very inconvenient, since when printing multi-page documents, the constant presence of the operator was required only to insert another sheet of paper into the printer and restart the printing process. In modern printers, the paper feeding process is automated. Before printing, you can place a stack of paper in the printer's output tray, the next sheet of which will be automatically picked up as needed and fed into the printing path. The number of sheets of paper that can be placed in the output tray differs in different printer models, but usually it is 50-100 sheets.
Drivers that control the printing process allow you to set the number of copies required and specify the pages or portions of pages that should be printed. Automation of the paper feeding process made using the printer extremely comfortable. These conveniences are especially noticeable when printing large volumes: just put paper in the output tray, specify print parameters and start the print program. The printer will do the rest automatically. Further development of the idea of automation led to the creation of printers that allow automatic printing using both sides of the sheet. True, such devices are still quite expensive and are used only in some expensive printer models.
Structurally, the paper feeder is designed differently in different types of printers, but there are two main designs, one or another version of which is used most often. Each of these schemes is convenient in its own way, and, at the same time, each is not free from some disadvantages.
Top-feed designs require a sufficient service area on top of the printer body, so such printers are poorly suited (or sometimes even unsuitable) for installation in alcoves with limited height. The receiving tray located below is often made folding, and sometimes is completely absent. With such a device, the printer takes up less space on the desktop, which is sometimes important. This design is used in Epson and Canon printers.
In bottom-feed schemes, the receiving tray is located above the feeder, which provides maximum convenience during operation. This tray layout is typical for most inkjet printers manufactured under the HP brand. The lack of need for an upper service area allows this printer to be installed in niches of limited height (equal to the height of the printer itself). The disadvantages of such printers include the fact that they take up more space on the desktop. Sometimes this is compensated by the ability to fold the receiving and supply trays when not in use. In such cases, to bring the printer into working condition, auxiliary operations are required to bring the trays into working position. Most HP printers do not fold the trays, ensuring they are always ready to use.
The synchronous interaction of all printer mechanisms, as well as its connection with the PC system unit, is ensured by the control device. This is a complex electronic device that is a mini-computer. It is this that carries out two-way exchange of information with a PC, storage and necessary transformations of information, and generation of control signals to the working parts of the printer.
To monitor the printer's status, control and display elements are usually provided. Control is carried out using buttons, and indication is via LEDs. The number of controls is usually small, and sometimes they are absent altogether, and the printer is controlled and its status is indicated using the PC itself.
All structural elements included in the printer are assembled on a metal chassis, which often serves as the bottom plane of the printer. The structural elements are covered with a plastic casing. The central part of the printer is occupied by the paper path. The drive elements are usually located on the left, and the head parking area is on the right side. Control and monitoring devices and control electronics are often located here. Typically, the layout of the printer is quite dense and, despite the seemingly large dimensions, there is practically no free space inside the printer. This circumstance sometimes forces you to make a remote power supply, which is less convenient to use. Built-in power supplies are usually installed in Epson printers; HP and Canon printers have a remote power supply.